Xylella fastidiosa: A Growing Threat to Global Agriculture
Xylella fastidiosa has emerged as one of the most devastating plant pathogens in modern agriculture, posing a significant threat to a wide range of economically important crops and native plant species. This gram-negative bacterium, which colonizes the xylem vessels of plants, is responsible for numerous diseases across diverse plant families, including economically crucial crops such as grapevines, citrus, olives, and various tree species.
The impact of Xylella fastidiosa on plant health is severe and often irreversible. By obstructing the plant’s water-conducting system, the bacterium causes symptoms such as leaf scorching, wilting, dieback, and eventual plant death. The insidious nature of Xylella infections lies in their ability to remain asymptomatic for long periods, allowing the pathogen to spread undetected through agricultural landscapes and natural ecosystems.
The economic consequences of Xylella fastidiosa infections are staggering. In affected regions, crop losses can be extensive, devastating local economies and threatening food security. Many agricultural industries have suffered significant losses due to the rapid spread of Xylella, leading to the destruction of crops and disrupting traditional agricultural practices.
The global agricultural industry faces unprecedented challenges in managing Xylella outbreaks. The bacterium’s wide host range, coupled with its ability to adapt to new environments and plant species, makes containment efforts extremely difficult. Furthermore, the role of insect vectors in transmitting the pathogen adds another layer of complexity to control strategies, necessitating integrated approaches that address both the pathogen and its vectors.
Climate change exacerbates the Xylella problem by potentially expanding the geographical range of both the bacterium and its insect vectors. This environmental shift could introduce the pathogen to new, vulnerable agricultural regions, further threatening global crop production and biodiversity.
As Xylella fastidiosa continues to spread across continents, the urgency for developing effective management strategies intensifies. The potential for this pathogen to affect multiple cropping systems simultaneously poses a significant challenge to global agriculture, necessitating coordinated international efforts in research, surveillance, and policy-making to mitigate its impact and prevent further spread.
Common Symptoms of Xylella fastidiosa Infection in Plants:
- Leaf scorch: browning and drying of leaf margins and tips, often progressing inward
- Chlorosis: yellowing of leaves, particularly between veins
- Stunted growth: reduced development of new shoots and leaves
- Wilting: drooping of leaves and stems, especially during warmer parts of the day
- Dieback: progressive death of branches from the tip downward
- Irregular leaf abscission: premature shedding of green leaves
- Reduced fruit size and quality in affected plants
- Delayed bud break in spring (in woody plants)
- Leaf mottling: irregular light and dark patches on leaves (in some species)
- Fruit discoloration and premature ripening (in fruit-bearing plants)
The severity and specific manifestation of these symptoms can vary significantly depending on the plant species, environmental conditions, and the particular strain of Xylella fastidiosa involved. It’s important to note that many of these symptoms, particularly leaf scorch and chlorosis, can be confused with other plant stresses such as drought, nutrient deficiencies, or other pathogens. Therefore, while these symptoms are indicative of potential Xylella infection, definitive diagnosis often requires laboratory testing. Early detection and proper identification of these symptoms are crucial for implementing timely management strategies and preventing the spread of the pathogen within agricultural settings and natural ecosystems.
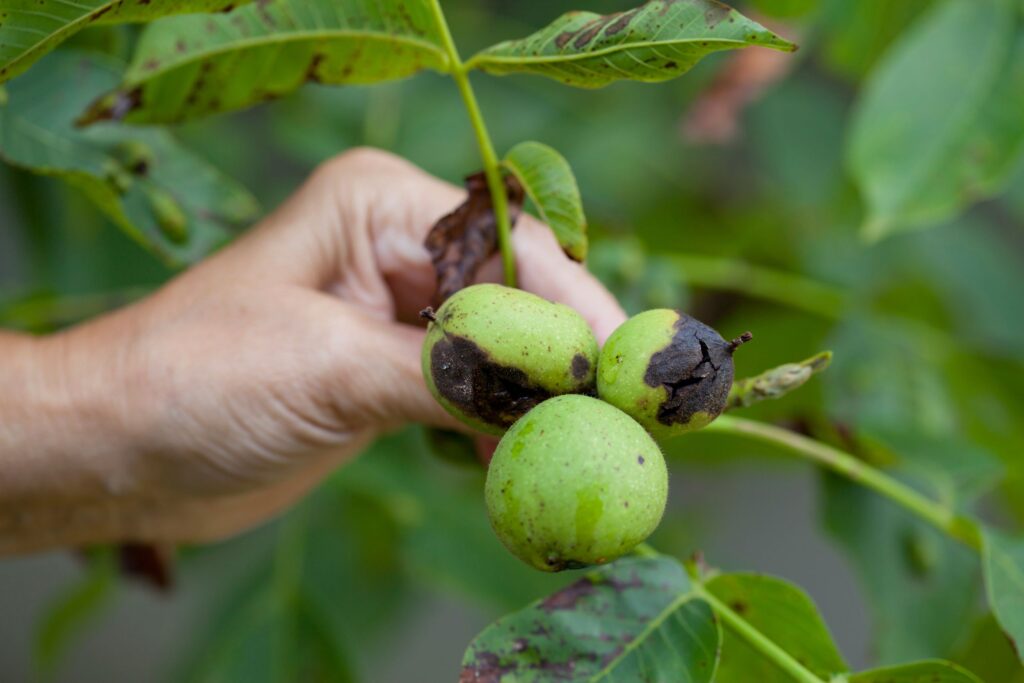


Limitations of Current Approaches
The treatment of Xylella fastidiosa presents significant challenges in modern agriculture, with traditional control methods proving increasingly inadequate. The bacterium’s ability to colonize the xylem vessels of plants makes it particularly difficult to target with conventional treatments. Current limitations in managing Xylella infections stem from the pathogen’s biology, its transmission methods, and the complexity of affected agricultural systems.
Chemical control measures, including antibiotics and copper-based compounds, have shown limited efficacy against Xylella fastidiosa. The bacterium’s location within the plant’s vascular system often renders topical treatments ineffective. Moreover, the overuse of these chemicals has led to concerns about environmental impact and the potential development of resistant bacterial strains, a process where the pathogen evolves to withstand previously effective treatments.
Vector control, aimed at managing the insect populations that spread Xylella, faces challenges due to the wide range of potential carriers and the difficulty in implementing large-scale insecticide applications without disrupting beneficial insect populations. This is particularly problematic in diverse agricultural landscapes and regions with strict pesticide regulations.
The removal of infected plants, a common practice in disease management, is often economically devastating, especially for crops with long maturation periods like olive trees and grapevines. This approach is particularly challenging for small-scale farmers who may lack the resources for large-scale replanting efforts.
The bacterium’s wide host range complicates the development of resistant plant varieties, as resistance genes effective in one species may not confer protection in another. This genetic diversity of both the pathogen and its hosts necessitates a multifaceted approach to breeding programs, requiring significant time and resources.
Climate change further exacerbates these challenges by potentially altering the distribution and behavior of both the pathogen and its vectors, making traditional management strategies less predictable and effective.
As existing methods prove increasingly inadequate, the urgent need for innovative, sustainable approaches to combat Xylella fastidiosa becomes ever more apparent. The complexity of this pathosystem demands continued research and the development of integrated management strategies to safeguard agricultural productivity and ecosystem health.
Learn how Qeen Biotechnologies' innovative bacteriophage solutions can help you effectively manage Xylella fastidiosa and protect your crops. Contact us today for more information.

Advanced Bacteriophage Therapy: Innovative Approach to Xylella fastidiosa Control
Qeen Biotechnologies has developed a bacteriophage therapy designed to combat Xylella fastidiosa infections across various agricultural systems. This solution utilizes specialized viruses that target X. fastidiosa, addressing the unique challenges posed by this xylem-dwelling pathogen. Our approach is tailored to the specific biology of X. fastidiosa, including its ability to form biofilms and its diverse strain variants.
The therapy is developed to overcome key obstacles in managing Xylella infections. It aims to reach the bacteria within the plant’s vascular system, a critical factor given X. fastidiosa’s location in the xylem. This targeted delivery system potentially offers a solution to the limitations of surface treatments and systemic chemicals that struggle to reach the pathogen effectively.
Environmental safety is a paramount consideration in our development process. The bacteriophages are meticulously selected for their specificity to X. fastidiosa, minimizing potential impacts on beneficial microorganisms in plant and soil ecosystems. This selective approach maintains ecological balance while focusing on pathogen control.
By offering this specialized bacteriophage therapy, Qeen Biotechnologies provides agriculturists with a new tool in the fight against Xylella fastidiosa. This approach represents a potential advancement in managing a pathogen that has proven resistant to conventional treatments, offering new possibilities for protecting vital crops and ecosystems from this pervasive threat.
How It Works
Qeen Biotechnologies’ bacteriophage therapy for Xylella fastidiosa utilizes a natural process of viral predation to control the bacterial population. This approach targets X. fastidiosa within the plant’s xylem vessels, where traditional treatments often fail to reach.
Infection
Replication
Lysis
This self-perpetuating process is especially valuable in managing X. fastidiosa, given its persistence in the xylem and the difficulty of reaching this environment with traditional treatments. The ongoing replication of phages provides sustained protection within the vascular system, addressing the chronic nature of X. fastidiosa infections in plants.
Qeen Biotechnologies
Benefits of Bacteriophage Therapy for Xylella fastidiosa Control
Bacteriophage therapy offers several advantages for managing Xylella fastidiosa infections, with specific benefits for affected agricultural systems:
Unlike broad-spectrum antibiotics, bacteriophages are highly specific to their bacterial targets. This precision targeting means:
- Selective elimination of harmful Pseudomonas bacteria, preserving beneficial microbes
- Minimized disruption to the body’s natural microbiome
- Reduced risk of opportunistic infections, such as Candida albicans overgrowth
Bacteriophages provide precision in pathogen control:
- Specifically targets X. fastidiosa strains within the xylem, preserving beneficial plant microbiota
- Effective against various X. fastidiosa subspecies affecting different crop species
- Potential for sustained action within the vascular system, crucial for long-term management
This therapy addresses limitations of vector control strategies:
- Directly targets the pathogen, reducing reliance on insect vector management
- Potentially effective in regions where vector control is challenging or restricted
- Complements existing integrated pest management programs
Bacteriophages offer unique capabilities in pathogen control:
- Potential to penetrate and disrupt X. fastidiosa biofilms within xylem vessels
- Addresses a key challenge in managing established infections
- May improve efficacy of other treatments by breaking down bacterial aggregates
This approach offers ecological and financial benefits:
- Naturally derived and biodegradable, minimizing environmental impact
- No toxic residues in plants or soil
- Potential to reduce crop losses in high-value perennial crops
- May decrease the need for widespread plant removal in affected areas
Bacteriophage therapy enhances overall plant health strategies:
- Potential for use in preventive and curative applications
- Adaptable to various crop systems affected by X. fastidiosa
- Compatible with different application methods suited to diverse agricultural practices
Phages provide a dynamic approach to pathogen control:
- Evolutionary potential to adapt alongside X. fastidiosa populations
- Possibility of developing phage cocktails to address strain diversity
- Offers an alternative to chemical treatments, reducing selection pressure for resistance
This therapy aligns with advanced agricultural practices:
- Supports trends towards biological control in crop protection
- Potential to enhance crop quality and yield in affected areas
- Promotes sustainable management of X. fastidiosa-susceptible crops
These distinctive advantages of bacteriophage therapy in X. fastidiosa control represent a novel approach in managing this challenging pathogen. By offering a solution that targets the bacterium within its xylem habitat, this method addresses key difficulties in current management strategies. As agriculture faces increasing pressure from X. fastidiosa spread, bacteriophage therapy emerges as a promising tool that combines targeted efficacy with environmental compatibility.
Cost-Efficient and Effective Regulatory Management
Qeen Biotechnologies’ bacteriophage therapy for Xylella fastidiosa control is designed with an emphasis on both cost-efficiency and strict regulatory compliance. This advanced approach reduces the financial burden associated with traditional control methods by decreasing the need for frequent chemical applications and intensive labor, thus enhancing overall cost-effectiveness.
Our therapy offers an alternative strategy for disease management that focuses on optimizing both efficacy and resource utilization. By effectively managing Xylella infections, we help farmers maintain productive crops, thereby minimizing economic losses due to this destructive pathogen.
From a regulatory standpoint, we ensure that our bacteriophage therapy aligns with all relevant agricultural regulations. Qeen Biotechnologies rigorously adheres to the highest standards in the development and application of our products, ensuring compliance with local and international guidelines governing plant disease control.
We work closely with regulatory bodies to certify that our bacteriophage products meet all necessary requirements for safe and effective use in agricultural settings. This dedication to regulatory compliance not only ensures the safety and reliability of our solutions but also provides farmers with the assurance that they are using a legally compliant product.
By integrating cost-efficiency with stringent regulatory standards, Qeen Biotechnologies delivers a sustainable and trustworthy solution for managing Xylella fastidiosa. Our commitment to regulatory excellence and economic practicality supports farmers in protecting their crops and optimizing their agricultural practices while adhering to all necessary regulations.
Seamless Integration with Agricultural Practices
Qeen Biotechnologies’ bacteriophage therapy for Xylella fastidiosa control is designed to fit seamlessly into your existing crop management systems. Our treatment is compatible with standard agricultural spraying equipment, making it easy to apply across various crops, including grapevines, citrus, olives, and many tree species.
This therapy is designed to be used alongside common agricultural inputs such as fungicides, insecticides, and fertilizers. This compatibility allows for potential tank-mixing, which can streamline application processes and reduce labor and operational costs. However, it is essential to follow specific guidelines to ensure the optimal performance of the bacteriophage treatment.
For best results, our bacteriophage therapy can be applied preventively to protect plants during critical growth periods or when environmental conditions favor disease development. It is also effective when used at the first sign of infection, providing flexibility and responsiveness in disease management strategies.
By integrating our bacteriophage therapy into your crop management practices, we aim to provide effective control of Xylella fastidiosa while enhancing overall efficiency. This approach not only helps in managing the disease but also supports sustainable agricultural practices by reducing the reliance on chemical treatments and minimizing environmental impact.
Proven Efficacy and Annual Testing
At Qeen Biotechnologies, we are dedicated to providing growers with effective and reliable solutions for managing Xylella fastidiosa. Our bacteriophage-based products undergo rigorous testing and evaluation to ensure their efficacy in controlling this devastating plant pathogen. We conduct extensive laboratory studies and field trials to validate the performance of our solutions under various environmental conditions and across different crops affected by Xylella fastidiosa.
In addition to our initial efficacy testing, we perform annual evaluations of our bacteriophage-based products to maintain the highest quality standards and ensure consistent performance. Our team of experts diligently monitors the efficacy of our solutions in the field, gathering data and feedback from growers who have incorporated our products into their disease management strategies. This ongoing testing and evaluation process allows us to continuously improve our solutions and adapt to the evolving needs of growers in their fight against Xylella fastidiosa.
Connect with Our Experts
Experiencing challenges with bacterial infections? Our team at Qeen Biotechnologies specializes in developing and producing bacteriophage-based therapies across various industries. Contact us to learn how our innovative approaches can address your specific needs.





